Best Vegan Protein Sources: Which Plant Proteins Are Best?
As a professional athlete and nutrition educator, I regularly choose vegan protein sources like beans, lentils, chickpeas, nuts, and seeds.
I have been using only vegan protein powder supplements for almost eight years.
Consuming a wide variety of adequate vegan protein sources is crucial for athletes like me or anyone looking to improve their health or appearance because they provide enough protein for building and maintaining muscle while also providing fiber, complex carbohydrates, unsaturated fats, and other micronutrients that are crucial for your health.
I still consume animal protein sources, and I am not a vegan or vegetarian, but regularly consuming a diet high in plant-protein sources has is key to my health and performance.
As the shift towards plant-based diets continues to gain momentum, finding high-quality vegan protein sources has become a significant focus for individuals looking to maintain or enhance their health.
Whether the motivation is health, ethical, or environmental, the demand for plant-based proteins is rising rapidly, and understanding how to meet protein needs through vegan options is more important than ever.
Protein is essential for numerous bodily functions, including building and repairing tissues, synthesizing hormones and enzymes, and maintaining muscle mass and immune health.
While animal-based proteins are often praised for being “complete” due to their comprehensive amino acid profile, many plant-based alternatives can provide sufficient protein and vital nutrients when consumed in a well-planned, balanced diet.
With the right combinations and choices, plant proteins can support optimal health, strength, and vitality.
Benefits of Choosing Vegan Protein Sources

Vegan protein sources not only provide essential nutrients but also offer a range of health benefits. Incorporating plant-based proteins into your diet can improve heart health, aid in weight management, and support a more sustainable environment, making them a powerful choice for overall well-being.
Heart Health
Studies have shown that plant-based proteins can improve cholesterol levels and lower blood pressure. Additionally, replacing animal protein with plant protein has been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease.
This makes vegan protein a heart-healthy option for those looking to improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Weight Management
Plant-based diets, which are naturally higher in fiber and lower in calories than animal-based diets, can aid in weight management. Vegan proteins are typically lower in saturated fat, which supports healthy weight loss or maintenance (Huang et al., 2020).
Additionally, the fiber content in plant foods promotes feelings of fullness, helping to manage hunger and calorie intake more effectively.
Environmental Sustainability
Aside from personal health benefits, plant-based proteins are more environmentally sustainable than animal-derived proteins. Plant-based diets have a lower carbon footprint, use fewer natural resources, and help reduce deforestation and biodiversity loss (Sabate & Soret, 2014).
By choosing vegan protein sources, individuals can positively impact the environment while nourishing their bodies.
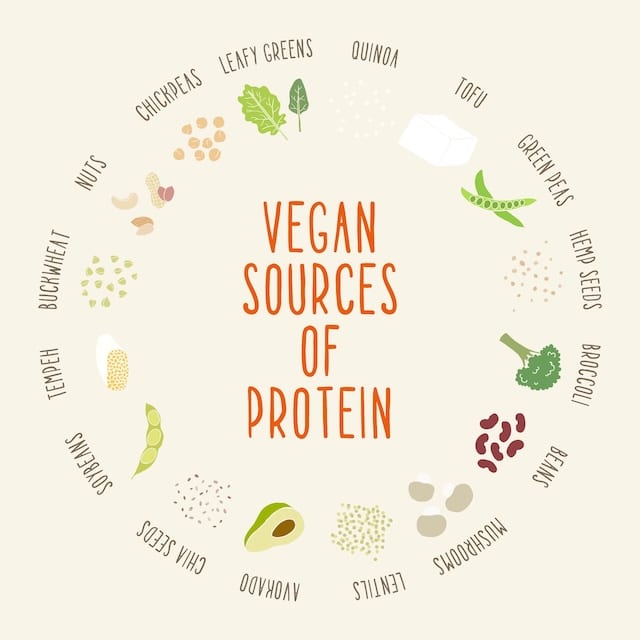
Best Vegan Protein Sources
Protein is vital for everyone, not just athletes or bodybuilders. It helps maintain muscle mass, supports immune function, and plays a key role in the body’s repair mechanisms. For vegans, obtaining enough high-quality protein can seem challenging, but with the right knowledge, it’s entirely feasible.
In fact, plant-based proteins are associated with numerous health benefits, including improved heart health and better weight management (Guasch-Ferré et al., 2019).
By incorporating a diverse array of plant proteins, vegans can achieve all the essential amino acids their bodies need. This guide will cover some of the best vegan protein sources and explain how to optimize your intake.
1.) Legumes: Beans, Lentils, and Chickpeas
Legumes are among the most versatile and protein-rich vegan foods. Beans, lentils, and chickpeas contain not only substantial protein but also essential micronutrients such as iron, fiber, and B vitamins.
Protein Content:
- Lentils: 18 grams of protein per cup (cooked)
- Chickpeas: 14.5 grams of protein per cup (cooked)
- Black beans: 15 grams of protein per cup (cooked)
Nutritional Benefits:
Beyond protein, legumes are excellent for digestion due to their high fiber content. They also contain important nutrients such as iron, potassium, and folate, making them a well-rounded option for those on a vegan diet (Iqbal et al., 2006).
Tip: Pairing legumes with whole grains can create a complete protein, giving you all nine essential amino acids your body needs.
2.) Quinoa: A Complete Protein
Quinoa is a powerhouse in the vegan world because it is one of the few plant foods considered a complete protein. This means it contains all nine essential amino acids that the human body cannot produce on its own (Bessada et al., 2019).
Protein Content:
- Quinoa: 8 grams of protein per cup (cooked)
Nutritional Benefits:
Quinoa is gluten-free and rich in magnesium, iron, fiber, and antioxidants, making it a perfect addition to any meal. It’s also versatile enough to be used in salads, soups, or as a side dish.
3.) Tofu, Tempeh, and Edamame: Soy-Based Proteins
Soy products, including tofu, tempeh, and edamame, are excellent vegan protein sources. These foods are derived from soybeans and provide all essential amino acids, making them another complete protein option (Lonnie et al., 2020).
Protein Content:
- Tofu: 10 grams of protein per half cup
- Tempeh: 21 grams of protein per half cup
- Edamame: 17 grams of protein per cup (cooked)
Nutritional Benefits:
Soy products are highly versatile and can be incorporated into both savory and sweet dishes. In addition to protein, soy products are rich in calcium, magnesium, and iron (Lqari et al., 2002). Tempeh, a fermented soybean product, is particularly beneficial for gut health due to its probiotic content.
4.) Seitan: A High-Protein Meat Substitute
Seitan, also known as wheat gluten, is one of the highest protein vegan foods available. It has a chewy texture and is often used as a meat substitute in vegan dishes.
Protein Content:
- Seitan: 25 grams of protein per 3.5 ounces
Nutritional Benefits:
Seitan is a fantastic source of protein, but it’s low in lysine, an essential amino acid. Pairing it with legumes or lysine-rich foods can help create a complete protein (Fleddermann et al., 2013). Due to its high gluten content, those with gluten intolerance or celiac disease should avoid seitan.
5.) Nuts and Seeds: Small But Mighty Protein Sources

Nuts and seeds are convenient vegan protein sources that offer healthy fats, fiber, and micronutrients like vitamin E and magnesium. However, they’re not complete proteins, so combining them with other vegan protein sources is essential.
Protein Content:
- Almonds: 6 grams of protein per ounce
- Chia seeds: 4.7 grams of protein per ounce
- Hemp seeds: 9 grams of protein per ounce
Nutritional Benefits:
In addition to protein, nuts and seeds are packed with omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and fiber. Hemp seeds, for instance, are a good source of omega-3s, which support heart health and reduce inflammation. Chia seeds, known for their ability to absorb water and expand, are excellent for hydration and digestion.
Tip: Add seeds to smoothies, oatmeal, or salads to boost both protein and healthy fat intake.
6.) Nutritional Yeast: A Vegan Pantry Staple
Nutritional yeast is a deactivated yeast commonly used in vegan cooking for its cheesy flavor. It’s also a surprising source of complete protein.
Protein Content:
- Nutritional Yeast: 8 grams of protein per 2 tablespoons
Nutritional Benefits:
Nutritional yeast is fortified with B vitamins, including B12, which is essential for vegans since it’s mostly found in animal products. Its high protein content and savory flavor make it a versatile addition to sauces, soups, and even popcorn.
7.) Spirulina: A Superfood Protein
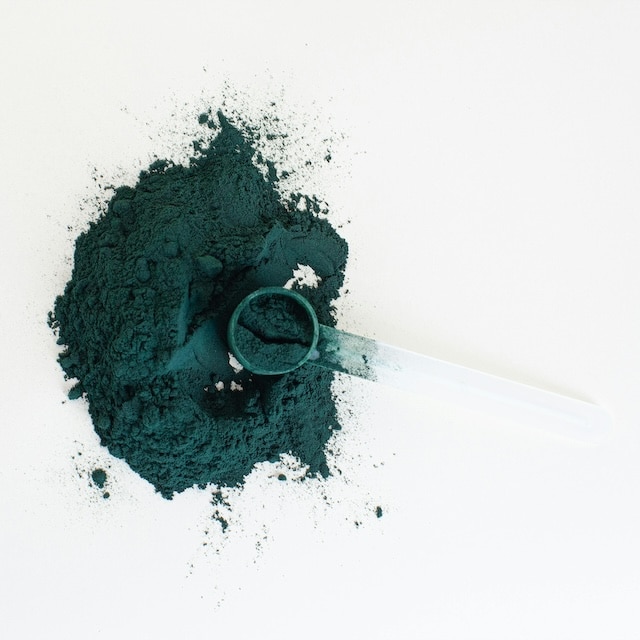

Spirulina, a blue-green algae, is often hailed as a superfood for its rich nutrient profile and high protein content. While not a complete protein on its own, it’s easily complemented by other plant-based proteins.
Protein Content:
- Spirulina: 4 grams of protein per tablespoon
Nutritional Benefits:
Spirulina is rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, including beta-carotene and B vitamins. It also contains iron, which is especially beneficial for vegans who may have difficulty meeting their iron needs through diet alone.
8.) Whole Grains: A Staple in Vegan Diets
Whole grains like brown rice, oats, barley, and farro may not be as protein-dense as legumes or soy-based products, but they still contribute a meaningful amount of protein to a vegan diet.
Protein Content:
- Oats: 5 grams of protein per half cup (dry)
- Brown rice: 5 grams of protein per cup (cooked)
Nutritional Benefits:
Whole grains are rich in fiber, B vitamins, and essential minerals such as magnesium and selenium (Paul et al., 2020). Their combination of complex carbohydrates and protein makes them ideal for sustained energy release, especially for athletes and active individuals.
9.) Peas: A Protein Powerhouse Beyond the Pod
Green peas are not just a side dish; they’re a potent source of vegan protein. Additionally, pea protein powder is becoming increasingly popular in vegan protein supplements.
Protein Content:
- Green peas: 8 grams of protein per cup (cooked)
Nutritional Benefits:
Peas are also rich in fiber, iron, and vitamins A and K, making them a nutrient-dense addition to meals. Pea protein powder, derived from yellow peas, is hypoallergenic and easy to digest, making it an excellent choice for those with soy or nut allergies.
10.) Buckwheat: A Gluten-Free, Protein-Rich Grain

Though its name suggests otherwise, buckwheat is not a type of wheat. It’s a gluten-free grain-like seed that’s high in protein and a great option for people with celiac disease or gluten sensitivity.
Protein Content:
- Buckwheat: 6 grams of protein per cup (cooked)
Nutritional Benefits:
Buckwheat is rich in antioxidants, fiber, and essential minerals such as magnesium and manganese. Like quinoa, it’s a complete protein, making it an excellent grain alternative for vegans seeking all essential amino acids.
How to Get Enough Protein on a Vegan Diet
Getting enough protein on a vegan diet can seem challenging, but with proper planning and mindful choices, it’s entirely achievable.
By diversifying plant-based protein sources, strategically combining foods, and using supplements when necessary, you can easily meet your daily protein requirements without relying on animal products.
Combine Protein Sources for Complete Nutrition
While some plant-based proteins are complete, others need to be combined to provide all essential amino acids. For example, pairing rice with beans or whole grain bread with peanut butter ensures you’re getting a full spectrum of amino acids.
Incorporating various foods that complement each other helps vegans achieve a balanced amino acid profile throughout the day.
Incorporate Protein at Every Meal
Ensuring that each meal contains a variety of plant-based protein sources will help maintain muscle mass and support overall health. For vegans, it’s crucial to spread protein intake throughout the day to optimize absorption and utilization.
This approach also ensures steady energy levels and supports proper muscle recovery after physical activity.
Use Vegan Protein Supplements
While it’s entirely possible to meet protein needs through whole foods, vegan protein supplements like pea protein, hemp protein, and soy protein powders can offer convenience and help fill gaps in your diet.
They are especially useful for athletes or individuals with higher protein requirements.
When comparing plant vs. whey protein, vegan options are plant-based and often easier to digest, while whey protein is animal-derived and known for its fast absorption rate.
Vegan protein supplements provide a quick, efficient way to boost protein intake, particularly on busy days or post-workout recovery.
Best Vegan Protein Powders
Vegan protein powders offer a convenient way to meet daily protein needs, especially for those with busy lifestyles, athletes, or anyone needing an extra boost.
Many options on the market provide high-quality plant-based protein without the artificial ingredients often found in traditional protein powders.
My two favorite vegan protein powders are Garden of Life Protein & Greens and OWYN Shakes. Both of these protein powder supplements offer unique benefits while supporting plant-based nutrition.
Garden of Life Raw Protein & Greens
Garden of Life Protein and Greens combines organic plant-based proteins with nutrient-dense greens, providing a powerful blend of nutrition. This powder contains 20 grams of protein per serving, sourced from peas, sprouted grains, and seeds, and also includes organic greens like spinach, alfalfa, and kale.
The added greens contribute to an extra dose of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, promoting overall health and vitality.
One of the key benefits of Garden of Life Raw Protein & Greens is its digestive enzymes and probiotics, which help improve digestion and nutrient absorption.
This makes it a suitable option for individuals who struggle with bloating or digestive discomfort after consuming protein supplements.
The formula is also free from gluten, dairy, and soy, making it accessible for people with food sensitivities.
Additionally, Garden of Life emphasizes the use of clean, organic ingredients with no artificial flavors or sweeteners, aligning with the preferences of health-conscious consumers looking for pure, plant-based nutrition.
Last update on 2025-04-18 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.
OWYN Shakes
OWYN Shakes (Only What You Need) are ready-to-drink vegan protein shakes that offer a convenient way to get a high dose of plant-based protein on the go. Each shake contains 20 grams of protein from pea, pumpkin seed, and flaxseed, making it a complete source of all nine essential amino acids.
This combination provides a balanced amino acid profile, which is crucial for muscle repair, recovery, and overall health.
OWYN Shakes also stand out for their added benefits beyond protein. They are rich in omega-3s from flaxseed, which support heart health, and contain prebiotic fiber, which aids digestion and supports gut health.
Each shake is fortified with superfoods like kale, spinach, and broccoli, offering a blend of vitamins and antioxidants that promote immune function and overall well-being.
These shakes are gluten-free, dairy-free, soy-free, and contain no artificial sweeteners, making them a top choice for individuals with dietary restrictions.
The variety of flavors, such as chocolate, vanilla, and cold brew coffee, also ensures there’s a delicious option for everyone.
Last update on 2025-04-18 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.