Anti-Inflammatory Diet Plan: Benefits, How to Eat, & More!
Anti-inflammatory diets are one of the most effective long-term strategies for preventing chronic disease, improving recovery, and enhancing overall vitality, whether you’re a professional athlete, someone with a demanding desk job, or anyone in between.
As a professional basketball player with a master’s degree in Nutrition Education, I’ve personally followed an anti-inflammatory diet for years to manage inflammation, speed up recovery after exercise, help control my asthma, and reduce the risk of injuries and illness.
These eating habits are not theoretical for me; they are deeply ingrained in how I fuel myself every day, in-season and off-season.
During my years playing professional basketball in Greece, Italy, Bulgaria, and North Macedonia, I experienced the Mediterranean diet in its most authentic form.
The natural, anti-inflammatory way of eating I adopted during those years has transformed how my wife and I cook and eat today.
Through evidence-based strategies and real-life application, I’ve learned how powerful anti-inflammatory diet plans can be in reducing systemic inflammation, supporting gut health, and regulating energy levels.
In this article, you’ll learn how to build an anti-inflammatory diet that actually supports healing, longevity, and a high-performance lifestyle.
What is Inflammation in the Body?
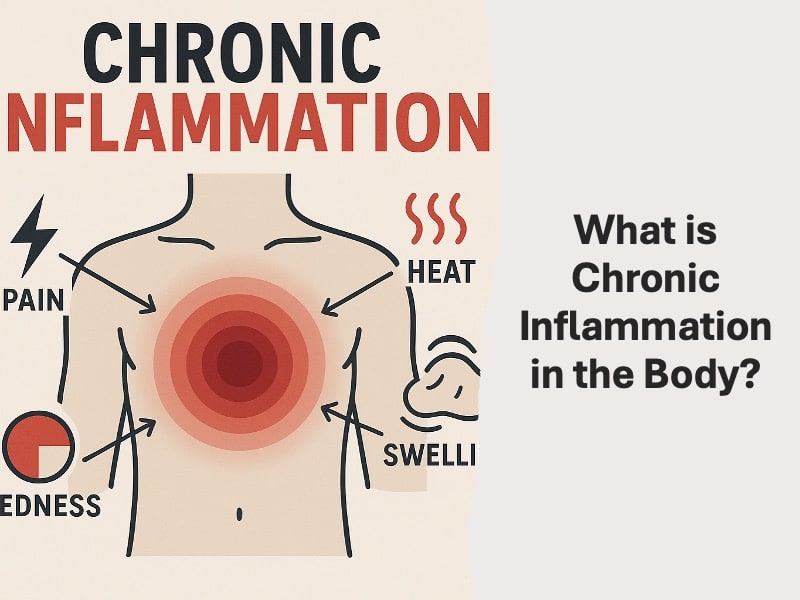
Inflammation is one of the biggest indicators of an illness in your body. When a foreign object such as a virus or bacteria enters your body, your body reacts by showing signs of fever, redness, swelling, and pain.
Inflammation is fine and even healthy as long as it’s targeting the disease.
However, when the inflammation starts to attack healthy cells, it can cause further chronic diseases in your body.
That’s why it’s important to understand the difference between acute and chronic inflammation and treat it accordingly.
Acute Inflammation
Acute inflammation is your body’s sudden response to an injury or illness that can cause sudden swelling, discoloration or flushed skin, pain, tenderness or fever in the affected area.
It goes away as soon as it appears, usually within a couple of hours to a few days.
It’s easy to manage and isn’t something you need to worry about.
Anything from a flu to a paper cut is likely to cause inflammation in the respective parts of your body as it heals the area.
Chronic Inflammation
Chronic inflammation on the other hand presents itself in the form of more serious symptoms like abdominal pain, fatigue, insomnia, skin rash, weight fluctuations, and even mood disorders.
This type of inflammation can last anywhere from a few months to several years if not managed properly.
Some diseases that can cause chronic inflammation include a variety of autoimmune diseases, cancers, cardiovascular ailments, and even mental health disorders (Harvard Health Publishing, n.d.).
While the symptoms themselves can present due to illnesses, there are multiple reasons for ailments that can be caused by your lack of care towards your body, and need to be managed actively to avoid severe inflammation.
Lifestyle Factors That Increase Inflammation
Whether you already have a disease, or just want to take care of your physical health, understanding the type of lifestyle factors that can increase inflammation in your body are important to live a healthier lifestyle.
Here’s a list of some habits that you may be guilty of, that can increase your risk of developing chronic inflammation:
- Smoking and Alcohol consumption: Excessive smoking has been linked to increased inflammation owing to the presence of carcinogens such as nicotine in it.
- High Cortisol Levels: High levels of cortisol caused by stress and an inactive production of sex hormones can enhance the markers of inflammation and make you more susceptible to ailments.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: A lack of physical activity in your daily life can contribute to obesity and excessive fat storage in your body, which is often associated with higher inflammation.
- Poor Gut Function: A lack of fibre rich diet can impact the quality of your gut biomes. Foods that are high in trans fats and sugar are more likely to cause inflammation in your body especially when consumed regularly.
- Lack of Sleep: A consistent lack of sleep can weaken your immune system, making it easier for you to fall into a pattern of chronic fatigue and inflammation.
- External Factors: Environmental toxins in polluted air, unclean water, and even soil with chemical fertilizers and pesticides can impact your body’s ability to create antibodies, fight off infections, and consequently, lead to chronic inflammation.
What is an Anti-Inflammatory Diet Plan?
An anti-inflammatory diet focuses on reducing chronic inflammation by prioritizing whole, nutrient-dense foods and eliminating ingredients known to trigger inflammatory responses.
Research shows a strong link between anti-inflammatory eating patterns and a lower risk of chronic, non-communicable diseases, including diabetes, hypertension, and certain autoimmune conditions (Medical News Today, n.d.).
Diets high in refined carbohydrates, added sugars, and trans fats can disrupt blood sugar balance and damage gut health by altering the microbiome, which is key to systemic inflammation.
In contrast, an anti-inflammatory diet supports immune function, improves gut integrity, and helps regulate inflammation at its source, making it an essential tool for long-term health and disease management.
The benefits of following an anti-inflammatory diet present themselves in the form of lowered risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and hypertension, and help manage the current symptoms of autoimmune diseases like hypothyroidism and psoriasis.
Benefits of Anti-Inflammatory Diets

An anti-inflammatory diet is more than just a nutritional trend—it’s a science-backed approach to improving health at the cellular level.
By emphasizing whole foods, healthy fats, and antioxidants, this way of eating can profoundly influence both short-term wellness and long-term disease prevention.
One of the most immediate benefits is reduced joint pain and muscle stiffness, especially for those dealing with arthritis or intense physical activity.
Lower systemic inflammation also supports faster recovery, improved digestion, and better energy regulation throughout the day.
Anti-inflammatory diets are also associated with a lower risk of developing chronic conditions such as type 2 diabetes, heart disease, neurodegenerative diseases, and certain autoimmune disorders.
These diets also help stabilize blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and support healthy cholesterol profiles.
In my experience as a professional athlete, adopting an anti-inflammatory approach has helped me stay resilient throughout long seasons, recover faster between games, and maintain a higher level of daily performance, both physically and mentally.
Ultimately, eating this way isn’t about restriction, it’s about choosing foods that help your body thrive and protect you against inflammation-driven health issues.
Best Anti-Inflammatory Foods To Add To Your Diet

Research has shown that foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, and certain vitamins and minerals fight inflammation and reduce common markers of inflammation such as C-protein, cytokines, and ESR (Calder, 2010).
Here’s a list of items you must include in your diet if you’re suffering from constant inflammation:
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
For a diet rich in omega-3, try to include seafood such as delicious fatty fishes.
For example, salmon, tuna, sardines, small freshwater shrimp, and even fresh whole lobster, which can be cooked and included with a variety of nuts and seeds in your meals as often as possible.
Antioxidant-rich Foods
Foods like blueberries, green leafy vegetables, green tea, dark chocolate, and whole grains are rich in antioxidants and should be consumed on a regular basis.
Nutrient-Dense Foods
Vitamins C, D, and E majorly found in citrus fruits, mushrooms, and spinach respectively can help reduce inflammation in your body.
If you’re dealing with chronic inflammation, minerals such as selenium, found in Brazil nuts and sunflower seeds, and magnesium from soy products and peanuts can improve your symptoms if consumed consistently.
Three Anti-Inflammatory Diet Plans That You Need To Know About
While there’s no one-size-fits-all approach to reducing inflammation, certain evidence-based eating patterns consistently show powerful anti-inflammatory effects.
These diet plans emphasize whole foods, healthy dietary fats, and phytonutrient-rich ingredients that support immune function and help manage inflammation long term.
Incorporating one of these anti-inflammatory diets into your lifestyle can improve recovery, protect against chronic disease, and elevate your overall health.
Plant-Based Diet
A plant-based diet is rich in plant protein, fiber, and phytonutrients, all of which have been linked to lower inflammation markers when compared with omnivorous diets, especially those that have red meat in them.
Multiple studies have indicated that vegetarians and vegans have a relatively reduced presence of C-protein, a primary marker of chronic inflammation.
When vegan diets are rich in spices such as ginger and turmeric, they further boost the body’s anti-inflammatory benefits.
Since a plant-based diet encompasses a variety of food styles ranging from veganism to vegetarianism, you can start by incorporating plant-based sources such as whole grains, vegetables and fruits into your diet.
To balance your diet, you must also include legumes, seeds, nuts, and oils.
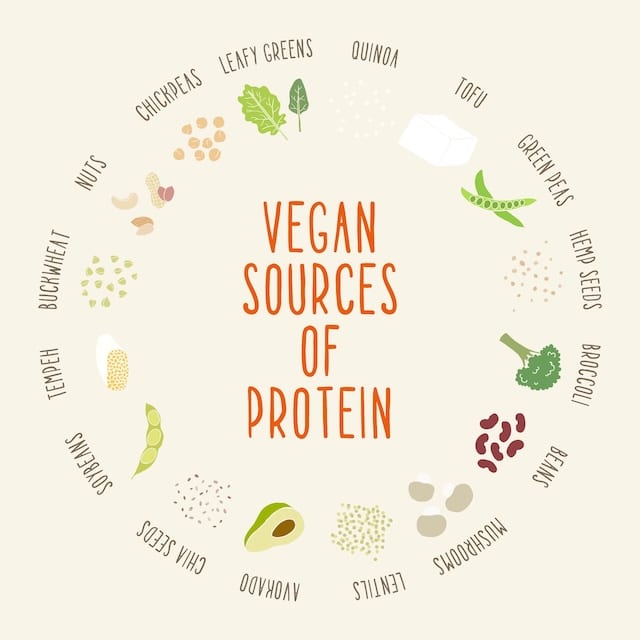
Since animal-based protein is excluded from a plant-based diet, it’s essential to include high-quality vegan protein sources such as legumes (beans, lentils, peas), soy products like tofu and tempeh, as well as nuts, seeds, and whole grains, all of which provide the amino acids needed for muscle repair, immune function, and overall health.
Mediterranean Diet
The Mediterranean diet is one of the most extensively studied anti-inflammatory eating patterns, known for its ability to support heart health, improved metabolic function, and promote longevity.
Its benefits span all age groups, with research showing that adherence during adolescence is linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases later in life (Yang et al., 2022).
This diet emphasizes anti-inflammatory foods that are rich in fiber, antioxidants, and healthy fats, which are key nutrients for managing inflammation and accelerating recovery.
From my personal experience living and playing professional basketball in Greece, Italy, Bulgaria, and North Macedonia, I’ve had the unique opportunity to experience the Mediterranean lifestyle firsthand.
During our time in these countries, my wife and I learned how to eat more intuitively and naturally, and the benefits for our health and recovery have been significant.
While Bulgaria and Macedonia blend Mediterranean and Slavic food cultures, the core principles remain: fresh, seasonal ingredients, minimally processed foods, and meals built around olive oil, herbs, legumes, vegetables, and fish.
Rather than restricting food intake, the anti-inflammatory Mediterranean diet plan approach encourages nutrient-dense substitutions.
Core ingredients include vegetables, fruits, legumes, lentils, whole grains, and nuts, along with generous amounts of extra virgin olive oil.
Fatty fish such as salmon, sardines, and mackerel provide omega-3s, while moderate amounts of poultry and, optionally, red wine add balance and flavor.
Following an anti-inflammatory Mediterranean diet plan can help regulate inflammatory markers, strengthen gut health, and serve as a sustainable foundation for long-term wellness.
The DASH Diet (Dietary Approaches To Hypertension)
DASH Diet (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension)
The DASH diet was originally developed to reduce high blood pressure, but its health benefits extend well beyond hypertension management.
It has consistently demonstrated the ability to lower inflammatory markers, improve cardiovascular function, and support overall health through whole food-based eating.
Research confirms its effectiveness: the PREMIER trial, DASH-Sodium study, and OmniHeart trial each found that DASH-style eating significantly lowers systolic and diastolic blood pressure, often by over 10 mmHg in hypertensive individuals.
A 2023 review in Cureus concluded that DASH also improves lipid profiles, lowers uric acid levels, reduces cardiovascular risk, and supports bone health through improved mineral balance (Onwuzo et al., 2023).
While the DASH diet recommends limiting sodium, it’s important to recognize that sodium is not inherently harmful, especially for active individuals.
As a professional athlete, I regularly consume salt in controlled amounts, particularly during periods of high sweat loss.
Sodium plays a critical role in hydration, muscle contractions, nerve signaling, and nutrient absorption.
Undereating salt, especially while exercising or sweating heavily, can lead to fatigue, cramping, and poor recovery.
Despite its salt restrictions, the DASH diet promotes a powerful anti-inflammatory foundation: it encourages fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins (such as fish and poultry), low-fat dairy, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
These foods are rich in antioxidants, magnesium, potassium, and fiber, which are key nutrients that reduce oxidative stress and promote immune resilience.
Unlike more restrictive diets, DASH allows for occasional sweets, with added sugars limited to five servings or fewer per week.
This makes it more realistic and sustainable for long-term use, even for those with a sweet tooth.
Key Points: The DASH diet remains one of the most evidence-based dietary strategies for lowering inflammation, reducing blood pressure, and promoting total-body wellness. It pairs well with personalized salt strategies and active lifestyles, particularly when balanced with hydration and recovery protocols.
Final Thoughts: Should You Try an Anti-Inflammatory Diet Plan?
Inflammation is a vital part of your body’s defense system, but when it becomes chronic, it can quietly drive a wide range of health issues, from fatigue and digestive problems to autoimmune diseases and cardiovascular conditions.
Reducing chronic inflammation requires more than just treating symptoms, and it starts with foundational lifestyle habits like regular exercise, stress management, quality sleep, and gut health support.
An anti-inflammatory diet is one of the most powerful, evidence-based strategies for addressing this issue at its root.
Diets like the DASH diet and Mediterranean diet have consistently shown the ability to lower inflammatory biomarkers, support immune function, and enhance recovery.
By focusing on whole foods rich in antioxidants, omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, and essential minerals, such as fatty fish, leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and legumes, you can lower systemic inflammation and build a stronger, more resilient body.
I’ve personally integrated these dietary habits into my life as a professional athlete, and the benefits have been clear: better recovery, more consistent energy, and long-term protection from chronic disease.
If you’re looking to improve how you feel and function each day, adopting an anti-inflammatory diet plan is one of the smartest steps you can take.



