The Simplest Diet Plan for Weight Loss: Rules You Can Actually Follow!
Losing weight can often feel overwhelming, but a well-structured diet plan for weight loss makes it more manageable. At its core, weight loss is simply about burning more calories than you consume, a principle known as the energy balance equation.
To support your journey, regular exercise is essential. It helps you burn extra calories, boosts your metabolism, and preserves muscle mass while you’re in a calorie deficit.
The challenge for most people lies in staying consistent with a diet plan for weight loss. Achieving long-term success requires following straightforward, sustainable rules that easily fit into your lifestyle.
How Your Diet Influences Weight Gain or Weight Loss
Weight gain or loss primarily depends on the balance between calories consumed and calories burned.
- If you consume more calories than you burn, the excess is stored as fat, leading to weight gain.
- Conversely, eating fewer calories than your body requires forces it to tap into fat stores for energy, resulting in weight loss.
Beyond calories, your diet affects hormones that regulate fat storage and energy use. For example, high-carb meals spike insulin, which promotes fat storage, while balanced meals with protein and fiber help stabilize insulin and support fat burning.
Hormones like ghrelin (which increases hunger) and leptin (which signals fullness) are influenced by diet quality—processed foods can increase hunger and lead to overeating, while whole foods improve satiety.
Protein-rich foods also aid weight loss by boosting calorie burn through digestion and preserving muscle mass, which helps maintain a higher metabolism.
Additionally, high cortisol from chronic stress can lead to cravings and fat storage, particularly around the abdomen.
Ultimately, a diet rich in whole foods helps regulate these hormones, supports fat loss, and improves long-term metabolic health, while processed, sugary foods promote fat storage and metabolic dysfunction.
What is a Good Weight Loss Diet Plan?
A good weight loss diet plan is a structured eating strategy designed to help individuals create a calorie deficit—consuming fewer calories than the body burns—to promote fat loss while preserving lean muscle mass.
It typically involves the intentional selection of foods and meal timing to optimize metabolic function, regulate appetite hormones, and encourage sustainable, long-term weight reduction.
Effective plans often emphasize:
- Whole foods (like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains)
- Portion control
- Consistent meal timing
- Limiting ultra-processed and high-sugar foods
- Supporting overall metabolic health and hormone balance
Rather than focusing solely on calorie restriction, the best diet plans incorporate nutrient density, satiety, and behavioral sustainability, aligning with long-term health goals rather than short-term results.
This approach supports fat loss while also improving insulin sensitivity, gut health, energy levels, and emotional well-being (Hall et al., 2019).
How to Make a Weight Loss Diet Plan
Creating an effective diet plan for weight loss involves more than just cutting calories—it requires building a structured, sustainable approach that supports your metabolism, reduces cravings, and helps you stay consistent long-term.
Here’s a research-backed framework to create your own weight loss diet plan:
Calculate Your Calorie Needs
To lose weight effectively, you need to create a consistent calorie deficit—burning more calories than you consume.
Start by estimating your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE) using an online calculator or the Mifflin-St Jeor equation, which considers your age, height, weight, gender, and activity level.
Once you have your TDEE, subtract 300–500 calories per day to safely target a loss of 0.5 to 1 pound per week.
This range is widely recognized as both sustainable and muscle-preserving, especially when paired with adequate protein and strength training.
For some individuals, losing 2 pounds per week may be achievable—especially in the early stages when water weight and glycogen stores drop—but losing faster than that increases the risk of muscle loss, metabolic adaptation, and weight regain.
To stay focused and on track, it’s also helpful to set SMART goals:
- Specific: Define exactly what you want to achieve (e.g., “Lose 8 pounds in 2 months”)
- Measurable: Track your progress with weight, measurements, or how clothes fit
- Achievable: Ensure your goal is realistic given your current lifestyle
- Relevant: Align it with your broader health or fitness aspirations
- Time-bound: Set a clear deadline for accountability and motivation
Using SMART goals alongside a calculated calorie deficit helps build structure, accountability, and momentum, which are key to long-term fat loss and health improvement.
Set Macronutrient Targets
Balancing protein, carbs, and fats improves satiety and metabolic health:
- Protein: 1.6–2.2 g/kg of body weight. Crucial for preserving muscle during a deficit and increasing satiety.
- Dietary Fats: ~20–35% of your total calories. Focus on sources like olive oil, avocado, nuts, seeds, and fatty fish.
- Carbohydrates: Fill in the remaining calories with complex carbs—fruits, vegetables, legumes, and whole grains.
Tracking your macros using tools like MyFitnessPal, Cronometer, or Macronutrient calculators can be helpful initially.
Build Your Meals Around Whole Foods
Structure each meal around:
- A lean protein source (chicken, tofu, eggs, fish, legumes)
- A fiber-rich carbohydrate (quinoa, oats, beans, starchy vegetables)
- A healthy fat source (nuts, olive oil, seeds)
- Non-starchy vegetables (spinach, broccoli, kale, peppers) for volume and micronutrients
This combination promotes satiety, supports blood sugar control, and reduces the urge to snack.
Plan for Meal Timing and Frequency
Eat in a way that supports energy and appetite regulation:
- 3 balanced meals per day with 1–2 small snacks works well for most people
- Avoid late-night snacking, which can impair metabolic flexibility and promote fat storage
- Consider early time-restricted feeding or intermittent fasting if it helps you stay consistent and reduce calorie intake naturally (Patterson & Sears, 2017)
Minimize Processed Foods and Sugary Beverages
Processed snacks, fast food, and sweetened drinks are calorie-dense, nutrient-poor, and disrupt hunger signals.
Replace them with water, unsweetened teas, and whole food snacks like fruit, yogurt, or nuts.
Include Flexibility and Enjoyable Foods
To maintain consistency, make room for foods you enjoy in moderation. A rigid plan increases the risk of burnout and binge episodes.
Aim for an 80/20 balance—80% whole, nutrient-dense foods, 20% enjoyable indulgences.
Track Progress and Adjust
Monitor your progress by tracking:
- Body weight and measurements (weekly)
- Energy levels, cravings, hunger (daily or weekly)
- Adherence to your plan
If your weight plateaus for more than 2–3 weeks, reassess your calorie intake or increase physical activity.
What Diet Plan is Best for Weight Loss?
Here are eight simple rules you can follow to lose weight and keep it off for good.
The best diet plan for weight loss is one that you can stick with consistently, supports your metabolic health, and aligns with your personal preferences, lifestyle, and activity level.
Research shows that adherence, rather than the specific macronutrient breakdown, is the strongest predictor of long-term weight loss success (Gardner et al., 2018).
Bottom Line: The best weight loss diet is not a one-size-fits-all plan. It’s a sustainable, enjoyable, whole-foods-based eating pattern that you can follow long-term and adapt as needed.
Here are evidence-based features of the most effective diet plans for fat loss:
Calorie Deficit Without Extreme Restriction
Your body needs fewer calories than it expends, but too steep of a deficit can cause muscle loss, metabolic adaptation, and burnout. Moderate calorie restriction is safer and more sustainable.
High in Protein
Protein supports satiety, reduces cravings, preserves lean muscle mass, and slightly boosts metabolism through the thermic effect of food.
Aim for 1.6–2.2g of protein per kilogram of body weight per day when losing weight.
Whole Foods-Based
Diet plans rich in whole foods—vegetables, fruits, legumes, lean meats, eggs, nuts, and whole grains—naturally control calories, enhance satiety, and regulate hunger hormones.
Minimally Processed
Minimizing ultra-processed foods helps prevent overeating, improves insulin sensitivity, and reduces inflammation. Ultra-processed foods are engineered to be hyper-palatable, making them easy to overconsume.
Low in Added Sugar and Liquid Calories
Reducing or eliminating sugary beverages and added sugars helps prevent blood sugar spikes and crashes, reduces cravings, and limits empty calories.
Supports Gut Health
A diet high in fiber, fermented foods, and prebiotics develops gut microbiota diversity, which is increasingly recognized as crucial for fat metabolism, inflammation control, and appetite regulation.
Flexible and Personalized
Intermittent fasting, Mediterranean, plant-forward, high-protein low-carb, or balanced macronutrient plans can all work—the key is personalization. Your dietary preferences, cultural background, activity level, and schedule should guide your choice.
The Most Effective Diet Rules for Weight Loss
Weight loss doesn’t have to be overly complicated. By focusing on simple, realistic rules—like limiting processed foods, cutting sugary drinks, eating whole foods, and staying hydrated—you can create a diet that works for your lifestyle.
Remember, it’s also important to remain flexible and avoid stressing over occasional missteps.
Consistency and balance are the keys to long-term success in managing your weight and overall health.
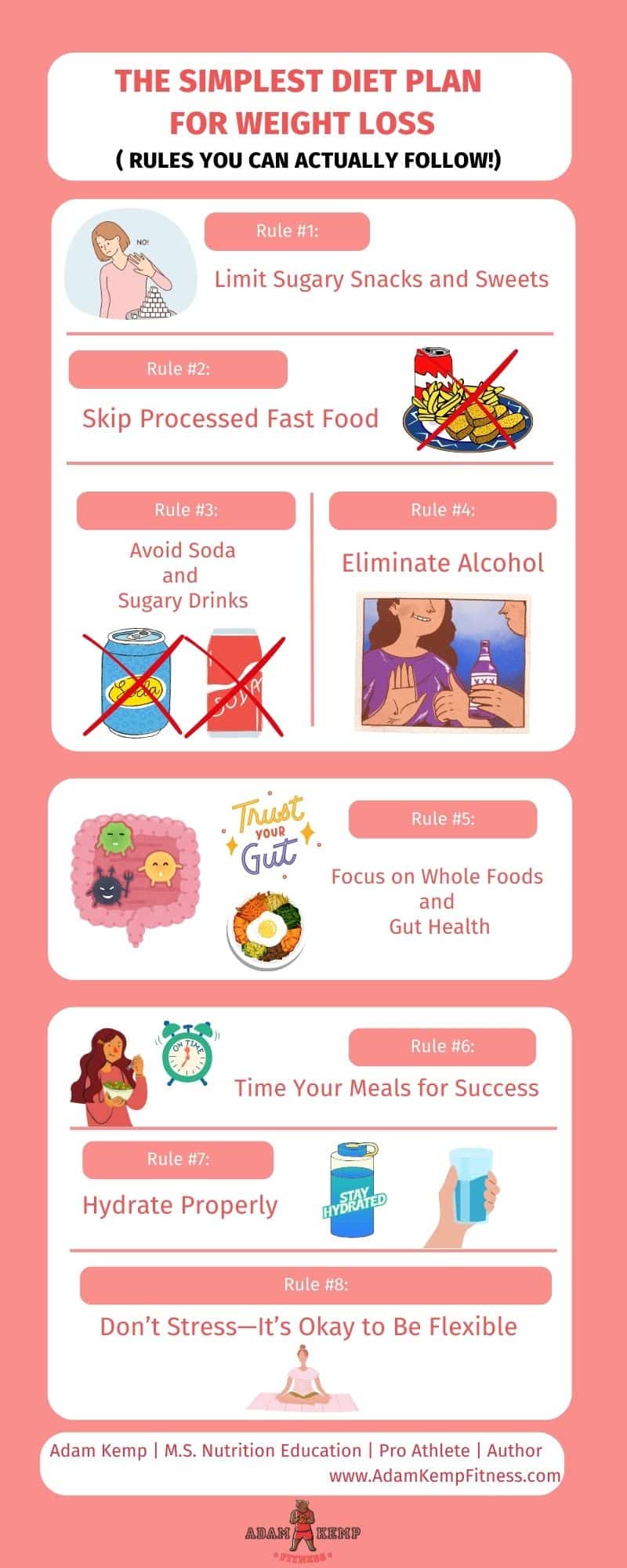
Rule #1: Limit Sugary Snacks and Sweets
Sugary snacks and sweets are loaded with empty calories that don’t provide any real nutritional benefit. These foods often cause sharp increases in blood sugar, which leads to energy crashes and more cravings, making it easier to overeat.
Limiting sugary treats can help stabilize your blood sugar, prevent overeating, and reduce overall calorie intake.
Instead of cutting sweets out entirely, opt for healthier alternatives. For example, fruit is naturally sweet and packed with fiber and vitamins.
This way, you satisfy your sweet tooth while fueling your body with nutrients that help with weight loss.
Rule #2: Skip Processed Fast Food
Processed fast foods are high in unhealthy fats, salt, and sugar, making them a big contributor to weight gain.
Not only do they pack on extra calories, but they also leave you feeling less satisfied, leading to overeating later in the day.
Regular consumption of fast food is also linked to inflammation, which can slow down your metabolism and make losing weight more difficult.
Cooking at home using whole, fresh ingredients is one of the best ways to avoid processed fast food.
Meal-prepping healthy options like lean proteins, vegetables, and whole grains is one of the best kitchen hacks, as it can save time and help you stay on track.
Rule #3: Avoid Soda and Sugary Drinks
Limiting salt intake is one of the most common diet myths because salt often gets the blame for problems caused by sugar.
Sugary beverages, such as soda, sweetened teas, and energy drinks, are a major source of hidden calories and cause a variety of health problems.
These drinks don’t make you feel full, yet they can dramatically increase your daily calorie intake.
Regularly consuming sugary drinks can cause weight gain over time, and even worse, it can make weight loss harder by increasing your cravings for more sugar.
The best alternative is to stick with water, black coffee, and unsweetened tea.
These beverages hydrate your body without adding extra calories. For those who work out often, low-calorie hydration drinks can provide electrolytes without derailing your diet.
Rule #4: Eliminate Alcohol

Alcohol is not only high in calories, but it can also hinder your weight loss progress by slowing down your metabolism and lowering your self-control, making it easier to indulge in unhealthy food.
Drinking alcohol affects weight loss as it impairs your body’s ability to burn fat and increases the likelihood of storing fat, particularly around your abdomen.
To stay on track with your weight loss goals, consider cutting alcohol from your diet altogether or significantly reducing your intake.
If you do choose to drink, moderation is key, and it’s important to be mindful of how it fits into your overall calorie intake for the day.
Rule #5: Focus on Whole Foods and Gut Health

Whole foods—like lean proteins, vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and healthy dietary fats—are naturally lower in calories and higher in nutrients compared to processed foods.
These foods keep you fuller for longer, which can help reduce the temptation to snack on unhealthy items.
Whole foods are also easier for your body to digest, helping your metabolism run smoothly.
Processed foods can be consumed occasionally but should be the exception, not the rule.
When choosing processed foods, focus on minimally processed options with simple ingredients.
Additionally, a healthy gut is crucial for effective weight loss.
Foods high in probiotics (such as yogurt, kefir, and fermented vegetables) help maintain a balanced gut microbiome, which supports digestion and helps control cravings.
Similarly, prebiotic-rich foods like garlic, onions, and oats nourish the good bacteria in your gut.
A healthy gut makes it easier to stay on track and avoid overeating.
Rule #6: Time Your Meals for Success
Meal timing can significantly impact weight loss success.
Late-night snacking is one of the easiest ways to derail your efforts, as your body processes food more efficiently earlier in the day.
Try to avoid eating late at night and instead focus on starting your day with a protein-rich, high-fiber metabolism-boosting breakfast.
This helps stabilize blood sugar levels and reduces hunger throughout the day, making it easier to maintain a calorie deficit.
A great way to kickstart your day is with a nutrient-packed smoothie.
Adding protein powder can help meet your protein needs, especially if you’re engaging in regular exercise.
High-protein, high-fiber meals keep you fuller longer and help maintain muscle mass as you lose weight.
Rule #7: Hydrate Properly
Staying hydrated is one of the simplest yet most important rules for weight loss. Water helps keep your metabolism active, curbs hunger, and improves digestion.
Often, people mistake thirst for hunger, leading them to eat more when their body actually just needs water.
For those who exercise frequently, low-calorie electrolyte drinks like Gatorade Fit or Prime Hydration can help replenish electrolytes without adding unnecessary calories.
Proper hydration not only aids in weight loss but also improves overall well-being and energy levels.

Rule #8: Don’t Stress—It’s Okay to Be Flexible
Finally, it’s important not to stress or feel guilty if you stray from your diet occasionally.
Weight loss is not a linear process, and your weight will naturally fluctuate day-to-day due to changes in water retention, hormone levels, and other factors.
Sometimes indulging in a favorite treat or meal is necessary to maintain a healthy relationship with food and avoid feelings of deprivation.
What’s important is getting back on track without guilt or self-criticism. Weight rebound and yo-yo dieting can lead to metabolic adaptations that make long-term weight management more difficult.
Being flexible and forgiving with yourself helps you stay consistent over the long term, which is essential for sustainable weight loss.
Final Thoughts: How to Stay Consistent with Your Weight Loss Diet Plan
The most effective diet plan for weight loss isn’t the one with the fewest calories or the trendiest restrictions—it’s the one you can follow consistently without sacrificing your physical or mental health.
Building healthy eating habits, such as eating whole foods, staying hydrated, managing stress, and being flexible with yourself, forms the foundation of sustainable fat loss.
Progress may not always be linear, but when your plan is rooted in balance, structure, and self-compassion, long-term success becomes far more achievable.
Start small, commit to simple changes, and trust the process. The results will follow.
If you’re serious about improving your health and finally making progress with weight loss, don’t miss my 7-Day Detox program. It’s a powerful, easy-to-follow system designed to help you break bad habits, reduce cravings, and create real, lasting change.

Get it for FREE by subscribing to my newsletter below!
You’ll instantly receive a 60-page eBook packed with actionable tips to reset your body and mind in just one week. Plus, you’ll get exclusive access to new articles, expert health and fitness tips, and behind-the-scenes insights I don’t share anywhere else.
Just enter your email below and take the first step toward a healthier, more energized you.
This website does not provide medical advice. This website site does contain affiliate links, and purchases may earn a commission.
Read my Medical Disclaimer, Review Disclaimer, and Publishing Policies for more details. Use of this site indicates acceptance of these terms.


