How to Burn Fat Fast: The Ultimate Guide to Fat Burning
If you’re searching for the most honest, effective, and scientifically sound way to burn fat fast—this is the resource you’ve been looking for.
As a professional athlete who has competed at a high level for over a decade, and as someone with a Master’s Degree in Nutrition Education, I’ve spent years fine-tuning my understanding of body composition, metabolism, and sustainable fat-burning strategies.
My experiences living and playing basketball across Europe have exposed me to a wide variety of cultural perspectives on food, fitness, and weight loss—helping me develop a comprehensive, evidence-based approach that works in the real world.
This guide isn’t about quick-fix weight loss gimmicks or unsustainable fads.
It’s about helping you understand the truth about fat burning so you can take control of your body and your health.
Whether you’re looking to improve your body composition, feel more energized, or finally break through a frustrating plateau, this article delivers actionable strategies to accelerate fat loss while maintaining lean muscle and enhancing long-term health.
From understanding the difference between burning fat and simply losing weight, to uncovering the role of macronutrients, sleep, gut health, and stress management—this is the most in-depth fat-burning guide you’ll find for free anywhere online.
Let’s cut through the noise and give you the tools to achieve your goals and burn fat as fast as possible!
What Is Fat Burning & How Fat Loss Happens
Fat burning refers to the biological process through which your body breaks down stored fat (adipose tissue) and converts it into usable energy.
This is the core of meaningful, sustainable fat loss—not just dropping water weight or muscle.
Understanding how this process works on a cellular level can help you make smarter decisions about your training, nutrition, and recovery.
The Science of Fat Storage
When you consume more energy (calories) than your body needs, the excess is stored—primarily as triglycerides in fat cells (adipocytes).
These triglycerides consist of three fatty acid molecules bound to a glycerol backbone, and they’re packed into fat cells to be used for energy in the future.
This is a normal and essential biological function—but when storage chronically exceeds demand, fat accumulates and body composition worsens.
How Fat Burning Works
To burn fat, your body must be in an energy deficit, meaning it needs more energy than is available from recent food intake.
Here’s what happens step by step:
Hormonal Signal: Lipolysis Begins
When your insulin levels drop (typically during a calorie deficit, fasting, or aerobic exercise), your body releases hormones like epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine.
These hormones bind to fat cell receptors and trigger lipolysis, the process of breaking down stored triglycerides.
Fat Mobilization
Triglycerides are split into free fatty acids (FFAs) and glycerol by enzymes like hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL).
These FFAs are released into the bloodstream and transported to tissues like muscle and liver.
Fat Oxidation for Energy
Inside cells, FFAs enter the mitochondria—the body’s energy factories—via a carrier molecule called carnitine (this is where L-carnitine supplements may offer support).
The fatty acids are then broken down in a process called beta-oxidation, producing ATP (adenosine triphosphate)—the usable energy currency of your body.
This entire process is commonly referred to as fat oxidation.
When Does Your Body Burn Fat?
Fat is burned most effectively when:
- You’re in a caloric deficit
- You’re doing moderate-intensity activity (like brisk walking or steady-state cardio)
- Glycogen stores are low, such as in fasted states or after longer-duration workouts
- Insulin levels are low and counter-regulatory hormones (like adrenaline) are elevated
Why Fat Burning Doesn’t Always Equal Fat Loss
Your body might burn fat for energy, but that doesn’t always translate to visible fat loss on your body.
True fat loss occurs when:
- Your body consistently mobilizes and oxidizes more fat than it stores
- Your net fat balance is negative over time
- You avoid re-storing fat by staying in a moderate energy deficit
If you burn fat during the day but overeat later, your body may simply re-store the fat—creating a cycle with no change in your physique.
Muscle vs. Fat as Fuel
During calorie restriction, your body will try to protect fat stores unless it’s signaled otherwise. That’s why it’s critical to:
- Eat adequate protein to preserve muscle
- Include resistance training to maintain lean tissue
- Avoid excessive cardio or prolonged starvation, which can lead to muscle breakdown
Muscle preservation ensures that your metabolic rate stays elevated, allowing you to continue burning fat efficiently.
Losing Weight vs Burning Fat: What’s the Difference?
Although many people use the terms “weight loss” and “fat burning” interchangeably, they refer to very different physiological processes—and understanding this difference is crucial for achieving real, lasting body transformation.
Weight Loss: More Than Just Fat Loss
Weight loss refers to a reduction in total body mass, which includes fat, muscle, water, and even bone density in extreme cases.
Most crash diets and extreme calorie restriction methods lead to rapid weight loss—but much of it comes from muscle tissue and water weight, not actual body fat.
This can result in a lower number on the scale, but not necessarily better health or an improved body composition.
When your goal is simply to lose weight without a strategy to preserve muscle, you can damage your metabolism and increase the likelihood of weight regain down the line.
Burning Fat: The Smarter, More Strategic Goal
Fat burning, on the other hand, refers specifically to the process of metabolizing stored adipose tissue—your body fat—for energy.
This typically occurs during moderate-intensity exercise, prolonged caloric deficits, or once glycogen stores are depleted.
Burning fat improves body composition, helping you become leaner, stronger, and more metabolically resilient.
When people say they want to “tone up,” “get lean,” or “look more athletic,” what they’re truly aiming for is fat loss with muscle retention—not just generic weight loss.
This guide will help you burn fat and get your dream body!
Why This Distinction Matters
Losing weight without focusing on fat loss can backfire. You risk slowing your basal metabolic rate (BMR), decreasing strength, and setting yourself up for fat rebound once you stop dieting.
By contrast, burning fat while maintaining or building muscle improves insulin sensitivity, protects your metabolism, and supports long-term weight management. This is the foundation for sustainable, healthy transformation.
The best strategies for fat loss focus on:
- A modest calorie deficit
- Strength training to preserve lean mass
- Adequate protein intake
- Smart, consistent cardio and NEAT (non-exercise activity thermogenesis)
Crash diets and excessive cardio may shrink your body—but they rarely sculpt it.
How to Lose Fat Fast Naturally and Permanently
Burning fat quickly without risking your long-term health isn’t just possible—it’s the most effective path to lasting results.
The key is shifting your mindset away from short-term fixes and toward evidence-based, habit-driven strategies that actually work.
Forget crash diets, starvation plans, or workouts that leave you broken down.
If you want to burn fat fast while maintaining your energy, strength, and sanity, here’s the approach that works—straight from a pro athlete who lives this every day.
Step 1.) Set a Clear, Measurable Goal
Burning fat starts with clarity.
You need a specific target, a timeline, and a plan.
Use SMART goals (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) to avoid vague intentions like “get fit” or “lose weight.”

Instead, define goals like:
- “Lose 10 pounds and drop 4% body fat in 10 weeks.”
- “Fit into size 32 pants by July while increasing lean muscle.”
Tools like the Bodypedia Smart Scale, DEXA scans, or even progress photos can help you track changes in body composition, not just body weight.
Step 2.) Create a Sustainable Calorie Deficit
Creating a calorie deficit is the foundational principle behind all successful fat loss. To burn fat, your body must use more energy (calories) than it takes in.
However, the way you create that deficit is what determines whether the result is lasting, healthy, and sustainable—or frustrating and short-lived.
Why a Moderate Deficit Is Most Effective
Drastically cutting calories may seem like the fastest route to results, but it often backfires.
Severe calorie restriction slows down your resting metabolic rate (RMR), increases cravings, reduces energy for workouts, and can trigger hormonal imbalances.
Worst of all, it increases the likelihood that you’ll lose muscle mass instead of fat.
Instead, aim for a moderate daily deficit of 300–500 calories below your maintenance level.
This is large enough to promote steady, healthy fat loss (about 1–2 pounds per week), while still giving your body enough nutrients and fuel to function optimally.
This slow-but-steady approach protects muscle tissue, minimizes the risk of metabolic adaptations to weight loss, and makes the process more sustainable—especially when combined with resistance training.
How to Calculate Your Calorie Deficit
Start by estimating your Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE)—the number of calories your body burns in a day including all activity. Then subtract 300–500 calories to establish your deficit.
You can calculate your TDEE using online tools, or use this rough formula:
- Men: TDEE ≈ 15–16 x body weight in pounds
- Women: TDEE ≈ 14–15 x body weight in pounds
If you weigh 180 pounds and you’re moderately active, your TDEE might be around 2,700. A 500-calorie deficit would bring you to 2,200 calories per day for fat loss.
Focus on Nutrient-Dense, High-Satiety Foods
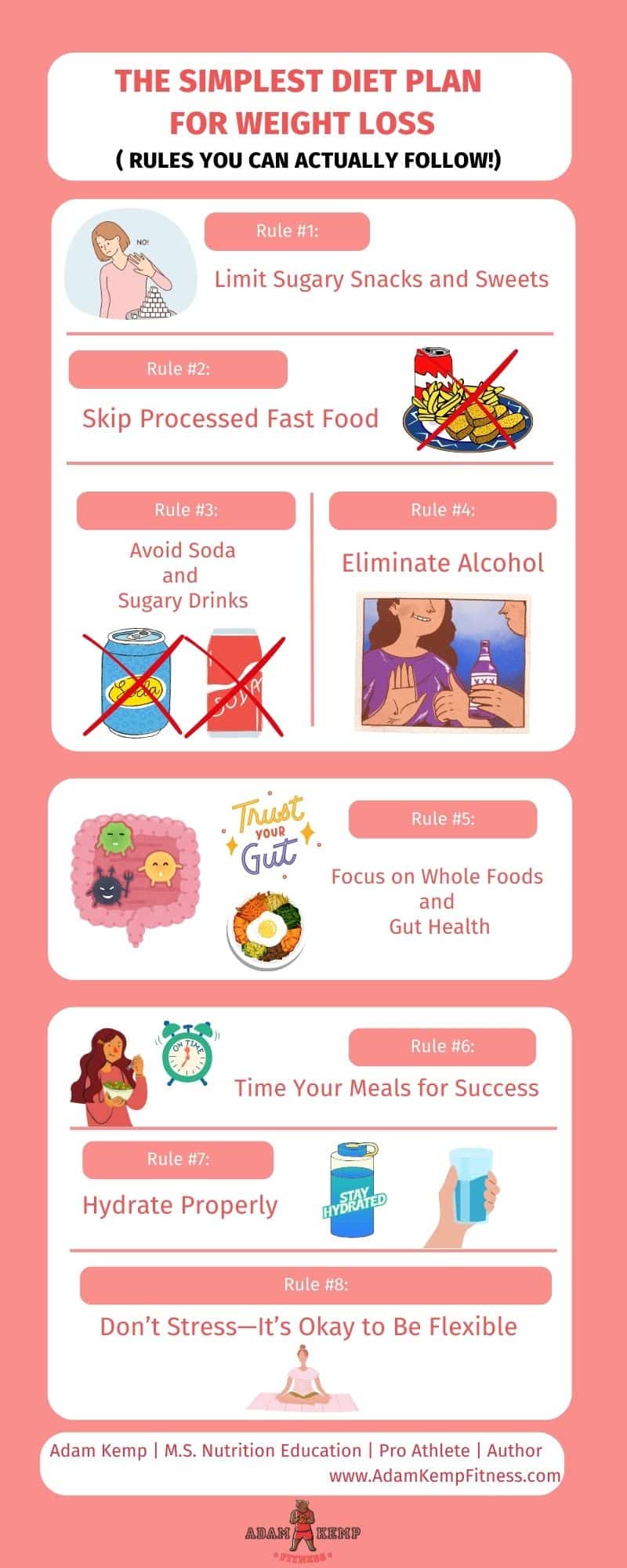
All calories are not created equal—not in terms of how they affect your hunger, metabolism, hormones, or long-term fat-burning potential.
To make a calorie deficit sustainable, your diet needs to do more than reduce calories—it must also nourish your body, support digestion, and keep you full and energized.
Prioritizing whole, nutrient-dense foods that offer a high degree of satiety (the feeling of fullness after eating) makes it dramatically easier to stay within your calorie target while still feeling satisfied, strong, and mentally sharp.
To make your calorie deficit easy to follow—and far more effective—construct each meal using this simple framework:
- Protein first
- Add fiber-rich plants
- Include healthy fats
- Hydrate before and with meals
- Use gut-supportive foods regularly
- Fill volume with low-calorie veggies
When you feed your body nutrient-dense, high-satiety foods, hunger becomes manageable, energy improves, and fat loss becomes a byproduct of your lifestyle—not a fight against it.
Here are key pillars to follow if you want to burn fat fast:
High-Protein Intake (the Cornerstone of a Fat-Burning Diet)
Protein isn’t just for muscle—it’s the most important macronutrient for preserving lean mass and curbing cravings during fat loss.
- Aim for 0.7–1.0g of protein per pound of body weight per day.
- Spread protein intake across 3–5 meals to optimize satiety and muscle protein synthesis.
- Include a variety of protein sources:
- Animal-based: eggs, poultry, fish, grass-fed beef, Greek yogurt, cottage cheese
- Plant-based: lentils, tofu, tempeh, seitan, beans, hemp seeds, quinoa
Why it works: Protein has the highest thermic effect of food (TEF)—up to 30% of its calories are burned during digestion and absorption. It also blunts hunger by reducing ghrelin (the hunger hormone) and increasing leptin (the satiety hormone).
Fiber-Rich Foods for Fullness and Blood Sugar Control
Fiber slows gastric emptying, improves blood sugar regulation, and helps support the gut microbiome—all of which reduce cravings and improve fat-burning capacity.
- Aim for at least 25–35g of fiber per day, or more if tolerated.
- Focus on a mix of soluble and insoluble fiber from:
- Legumes: lentils, black beans, chickpeas
- Whole grains: oats, barley, quinoa
- Vegetables: broccoli, Brussels sprouts, carrots, spinach
- Fruits: berries, apples, pears
- Seeds: chia seeds, flaxseed, psyllium husk
High-fiber diets also help nourish beneficial gut bacteria, which are directly linked to improved metabolic health, reduced inflammation, and better energy extraction from food.
Healthy Fats That Regulate Hormones and Satiety
Dietary fat has been unfairly demonized for years, but the right types of fat play a critical role in weight regulation and fat metabolism.
- Focus on monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, which support hormonal balance, slow digestion, and keep hunger at bay.
- Excellent fat sources include:
- Avocados
- Extra virgin olive oil
- Fatty fish like salmon or sardines
- Nuts and seeds (almonds, walnuts, flaxseeds)
- Nut butters (in moderation)
Fat is calorie-dense (9 kcal/gram), so portion control still matters—but including some in every meal enhances satiety and can prevent overeating later in the day.
Low-Energy-Density Foods: More Volume, Fewer Calories
Low-energy-density foods allow you to eat larger volumes of food for fewer calories—helping you stay fuller without breaking your calorie deficit.
These foods are typically high in water and fiber, but low in fat and added sugars.
Prioritize:
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale, romaine)
- Cruciferous veggies (cauliflower, cabbage, broccoli)
- Broth-based soups
- Berries and melons
- Zucchini, cucumbers, celery
Using these foods to bulk up meals increases your plate size and satiety—without loading up on unnecessary calories.
Hydration: The Overlooked Secret to Appetite Control
Staying well-hydrated is critical for fat loss, digestion, performance, and hunger regulation.
Even mild dehydration can mimic hunger and lead to unnecessary snacking or overeating.
Drinking enough water also supports metabolic processes like lipolysis—the breakdown of fat cells for energy.
- Drink at least half your body weight (lbs) in ounces of water per day.
(e.g., 180 lb person = ~90 oz/day) - Drink a large glass of water 20–30 minutes before meals to naturally reduce calorie intake.
- Limit liquid calories from sugary drinks, lattes, and alcohol.
Bonus beverages that increase metabolism and fat burning:
- Green tea and oolong tea (rich in catechins)
- Black coffee (appetite-suppressing and thermogenic when unsweetened)
- Sparkling water or herbal tea as calorie-free ways to reduce cravings
- Celsius Energy Drinks: Celsius drinks burn fat and are evidence-based to promote fat burning. They contain 200mg of caffeine per can, so you have to watch out for total daily caffeine consumption.

Support Your Gut Microbiome with Prebiotics & Probiotics
An often-overlooked piece of fat loss: your gut health.
A balanced gut microbiome can improve insulin sensitivity, hunger hormone regulation, inflammation control, and fat oxidation.
When your gut is thriving, your entire metabolism works more efficiently.
Include prebiotic foods that feed beneficial gut bacteria:
- Onions, garlic, leeks, asparagus, chicory root, apples, oats
And consume probiotic-rich fermented foods to populate the gut with healthy microbes:
If whole-food sources aren’t enough, a combined prebiotic + probiotic supplement like BIOHM Super Greens with Probiotics may support fat-loss efforts, especially in people with digestive imbalances.
Last update on 2025-04-29 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.
Watch Out for “Hidden Calories”
To maintain your calorie deficit, it’s critical to monitor the sneaky ways calories can creep into your day:
- Liquid calories from juices, sugary coffee drinks, and alcohol
- “Healthy” snacks like granola bars or trail mix that are calorie-dense
- Cooking oils and dressings that add 100–300+ calories per meal
Track your intake (even loosely) using tools like Cronometer, MyFitnessPal, or Carbon Diet Coach to stay accountable and aware of what’s working.
Refeed Days & Adjustments
Occasionally, incorporating a refeed day—where you increase calories to maintenance levels (mostly from carbohydrates)—can help restore leptin levels, reduce mental fatigue, and support training intensity.
These should be structured and used strategically, not as a license to binge.
As your bodyweight drops, your calorie needs will gradually decrease. Reassess your TDEE every 4–6 weeks and adjust your intake to maintain a consistent deficit.
Supplements for Fat Burning
Burning fat while holding on to lean muscle is one of the most difficult challenges in fitness.
Even with a calorie deficit and intense training, achieving a shredded, aesthetic physique often requires targeted support for metabolism, recovery, gut health, and hormonal balance.
That’s why this cutting stack works—it combines the most effective, natural supplements to help your body burn fat more efficiently, reduce inflammation, control appetite, support digestion, and preserve lean mass.
Rather than relying on stimulants, this approach works with your body by optimizing the systems that influence fat metabolism, muscle maintenance, and energy production.
This fat burning stack is designed to address five key factors that determine fat loss success: muscle retention, metabolic rate, appetite regulation, digestive efficiency, and hormonal health.
When these elements are aligned, it becomes easier to stay in a calorie deficit, train hard, and recover well—without experiencing burnout or rebound weight gain.
Garden of Life Raw Protein & Greens
At the core of the stack is Garden of Life Raw Protein & Greens, a plant-based protein powder that delivers a complete amino acid profile to support muscle retention during calorie restriction.
The added greens provide essential nutrients and antioxidants that support detoxification, immune health, and digestion—important for recovery and long-term sustainability.
Last update on 2025-04-29 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.
Force Factor Colostrum
To further support gut health and metabolism, Force Factor Colostrum strengthens the intestinal lining, promotes the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, and improves nutrient absorption.
A healthy gut microbiome is closely tied to insulin sensitivity, inflammation control, and metabolic efficiency, all of which are essential during a fat-loss phase.
Last update on 2025-04-29 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.
RSP AminoLean
For clean energy and enhanced fat oxidation, RSP AminoLean is ideal.
AminoLean helps you stay energized for workouts, boost metabolism, and reduce cravings throughout the day.
RSP AminoLean provides essential amino acids to preserve lean muscle while combining natural fat-burning ingredients like caffeine, L-carnitine, green tea extract, and CLA to support metabolism and energy production.
It’s an excellent all-in-one supplement for maintaining performance during a calorie deficit without relying on excessive stimulants.
Last update on 2025-04-29 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.
Xtend Ripped
To prevent muscle breakdown and speed up recovery, Xtend Ripped offers BCAAs combined with ingredients like capsaicin and CLA for targeted fat-burning support.
This supplement ensures that the weight you lose during cutting comes from fat, not hard-earned muscle.
Last update on 2025-04-29 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.
Bloom Greens & Superfoods or BIOHM Super Greens
Bloom Greens & Superfoods or BIOHM Super Greens with Probiotics optimize digestion and nutrient absorption by combining probiotics, digestive enzymes, and micronutrient-rich greens.
This helps reduce bloating, supports the gut-brain axis, and ensures the nutrients from your food and supplements are actually used effectively.
Last update on 2025-04-29 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.
Last update on 2025-04-29 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.
Naturewise Turmeric Curcumin
For inflammation control and metabolic support, Naturewise Turmeric Curcumin helps reduce systemic inflammation, which is often elevated during periods of stress, hard training, or calorie restriction.
Lower inflammation means better recovery, improved insulin sensitivity, and a more efficient fat-burning process.
Last update on 2025-04-29 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.
Sports Research Vitamin D3 + K2
Hormonal balance is supported by Sports Research Vitamin D3 + K2, which plays a critical role in testosterone production, energy regulation, and calcium metabolism.
Vitamin D deficiency is common and linked to increased fat storage, while K2 ensures calcium is directed to bones and not soft tissues—essential for anyone training hard.
Last update on 2025-04-29 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.
Bulk Supplements CLA
Finally, Bulk Supplements CLA helps improve body composition by enhancing fat metabolism and preventing fat regain during periods of calorie restriction.
Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) supports lean mass retention and has been shown to aid in breaking down stored body fat for energy.
If you are trying to burn fat and improve your body composition, Conjugated Linoleic Acid (CLA) is important because it may inhibit the activity of lipoprotein lipase (LPL)—an enzyme responsible for transporting and storing fat into adipose tissue.
By reducing LPL activity, CLA helps decrease the amount of fat stored in fat cells, promoting the use of fatty acids for energy instead of storage.
Last update on 2025-04-29 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.
Step 3: Prioritize Resistance Training and Smart Cardio
Exercise is not just about burning calories—it’s about signaling your body to build muscle, improve metabolic flexibility, and favor fat oxidation over muscle breakdown.
While nutrition creates the conditions for fat loss, movement determines the quality of that loss.
When done strategically, a combination of resistance training, cardio, and NEAT (Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis) forms the ultimate fat-burning routine.
Why Resistance Training Is Non-Negotiable
Weight training during a calorie deficit sends a clear message to your body: preserve lean mass.
Without this signal, your body is more likely to break down muscle tissue alongside body fat.

Benefits of resistance training for fat loss include:
- Muscle preservation, which prevents metabolic slowdown
- Increased resting metabolic rate (RMR), meaning you burn more calories even at rest
- Improved insulin sensitivity, helping your body store less fat and use more for energy
- Post-exercise oxygen consumption (EPOC)—the “afterburn effect”—which increases calorie burn for up to 24–48 hours post-workout
How to Resistance Train for Fat Burning
For optimal fat loss, prioritize compound exercises that recruit large muscle groups and stimulate a significant hormonal and metabolic response.
Some of the best exercises for weight loss and fat burning include:

Structure your workouts with 3–5 compound movements, performed in 3–4 sets of 8–12 reps, with controlled rest periods to maintain intensity.
You can also include supersets or circuit training to elevate your heart rate while building muscle—effectively combining resistance training with cardio for enhanced fat burning.
Train at least 2–4 times per week, ensuring full-body stimulation and adequate recovery between sessions.
Incorporate Smart Cardio for Efficient Fat Loss

Cardio workouts support fat loss by increasing total daily energy expenditure (TDEE), improving cardiovascular health, and mobilizing fat stores during aerobic activity.
The key is choosing the right type and dosage for your body and goals.
Low-Intensity Steady-State Cardio (LISS)
LISS involves working at a steady, moderate pace—typically 60–70% of your max heart rate—for 30–60 minutes.
Examples:
- Brisk walking
- Light jogging
- Steady cycling
- Elliptical machine workouts
- Incline treadmill walking
LISS cardio primarily relies on fat as a fuel source, making it a powerful tool for increasing daily energy expenditure without spiking cortisol or fatiguing your nervous system.
LISS is especially valuable on rest days or as a morning fasted walk to gently stimulate fat oxidation.
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT)

High-intensity interval training (HIIT) alternates short bursts of all-out effort with periods of rest or low-intensity movement.
A typical HIIT session:
- 30 seconds sprint or jump squats
- 90 seconds light recovery
- Repeat for 15–25 minutes
Benefits of HIIT include:
- Maximized calorie burn in less time
- Increased EPOC (calories burned post-workout)
- Enhanced mitochondrial efficiency and fat oxidation
- Improved insulin sensitivity and metabolic rate
Start with 1–2 HIIT sessions per week. More is not always better—especially if it impairs recovery or leads to burnout.
There are many great HIIT workouts and interval strategies, but my favorite is Tabata workouts.
NEAT: The Overlooked Fat-Burning Powerhouse
NEAT (Non-Exercise Activity Thermogenesis) refers to the calories you burn during non-structured movement throughout the day—everything from walking your dog to pacing while on the phone.
Unlike gym workouts, NEAT can be maintained for hours and significantly impacts total fat loss over time.
NEAT can account for up to 15–50% of your TDEE, depending on your lifestyle.
To increase NEAT:
- Take walking breaks every hour
- Use a standing desk or walk during phone calls
- Park farther away from entrances
- Take the stairs
- Walk after meals (this also improves blood glucose regulation)
- Set a daily step goal (e.g., 8,000–12,000 steps/day)
Many people plateau in fat loss not because of what they’re eating or how they’re training, but because their NEAT unintentionally drops during a calorie deficit.
Staying active outside the gym helps maintain a robust fat-burning metabolism.
The Winning Combo: Resistance, Cardio & NEAT
The most effective fat-burning routine includes:
- 2–4 resistance training sessions per week (heavy, compound-focused)
- 2–3 LISS cardio sessions (30–60 min)
- 1–2 HIIT sessions (15–25 min)
- Daily NEAT movement (steps, chores, walking, standing, fidgeting)
This blended training strategy preserves muscle, accelerates fat loss, and improves metabolic flexibility without causing excessive fatigue or burnout.
Combined with proper nutrition, this movement pattern creates an ideal internal environment for burning fat fast—and keeping it off permanently.
Step 4.) Sleep Well and Manage Stress
Fat burning isn’t just a matter of calories and reps—it’s also deeply affected by how well you recover and how your nervous system responds to stress.
If you’re training hard and eating right but not seeing results, poor sleep and hronic stress might be holding you back more than you realize.
Sleep: The Fat-Loss Accelerator Most People Ignore
Getting 7–9 hours of high-quality sleep per night is non-negotiable for optimal fat burning. Sleep regulates the key hormones that influence hunger, satiety, metabolism, and energy storage.
When sleep is restricted:
- Ghrelin (the hunger hormone) increases
- Leptin (the satiety hormone) decreases
- Cortisol rises, increasing fat storage (especially in the abdomen)
- Insulin sensitivity worsens, making it harder to burn fat and control blood sugar
Even one night of poor sleep can impair your body’s ability to regulate appetite and blood glucose the next day—leading to more cravings, slower metabolism, and decreased workout performance.
Tips to Improve Sleep Quality:
- Set a consistent bedtime and wake time, even on weekends
- Avoid screens at least 30–60 minutes before bed
- Limit caffeine after 2 p.m.
- Keep your bedroom cool, dark, and quiet
- Use a sleep tracker (like Whoop, Oura, or Sleep Cycle) to improve sleep habits
Natural sleep aids can further support your ability to fall asleep faster, stay asleep longer, and wake feeling refreshed—without the side effects of prescription sleep medications.
Research-backed supplements like melatonin, magnesium glycinate, magnesium threonate, and calming herbs work by relaxing the nervous system, reducing stress hormone levels, and improving sleep architecture—the structure and quality of sleep cycles.
Melatonin is a hormone naturally produced by the pineal gland in response to darkness. It helps regulate your circadian rhythm, signaling to your body that it’s time to rest.
Supplementing with 1–3 mg of melatonin before bed has been shown to improve sleep latency (how quickly you fall asleep) and sleep efficiency, especially for people experiencing insomnia or jet lag (Ferracioli-Oda et al., 2013).
It’s best used occasionally or during times of disrupted schedules, not as a nightly dependency.
Magnesium plays a key role in muscle relaxation, GABA activity, and calming the central nervous system.
Research indicates that magnesium supplementation can improve total sleep time, sleep onset latency, and sleep quality, especially in older adults or those with insomnia (Abbasi et al., 2012).
Two forms stand out for natural sleep support:
- Magnesium Glycinate: Chelated with glycine, this form is highly bioavailable and has dual calming effects on the nervous system. Glycine itself is known to lower core body temperature and improve sleep depth, while magnesium reduces cortisol and enhances GABA activity. Magnesium glycinate is gentle on digestion and ideal for nighttime use.
- Magnesium L-Threonate: This form is notable for its ability to cross the blood-brain barrier, making it especially effective for cognitive relaxation and sleep initiation. Studies suggest magnesium threonate may support deep sleep cycles and memory consolidation by increasing brain magnesium levels.
Supplementing with either form can help reduce nighttime restlessness, muscle tension, and anxiety—allowing for a deeper, more restorative sleep.
My favorite magnesium supplement is Qunol Magnesium Glycinate (420mg):
Last update on 2025-04-29 / This article includes affiliate links/Images via Amazon Product Advertising API. I may earn commissions on purchases made through these links.
Recovery = growth. You don’t get stronger, leaner, or healthier in the gym—you get stronger when you sleep.
Stress: The Hidden Roadblock to Fat Burning
Chronic stress doesn’t just affect your mood—it directly impacts your body’s ability to lose fat through hormonal disruption.
When your brain perceives stress (mental, emotional, or physical), your adrenal glands release cortisol to help you cope.
In the short term, cortisol is helpful. But when it stays elevated for days or weeks, it can:
- Trigger fat storage, particularly in the abdominal region
- Increase ghrelin, leading to cravings and overeating
- Cause insulin resistance, impairing fat burning
- Suppress thyroid function and metabolism
- Disrupt sleep patterns, worsening recovery and energy
Practical stress-reduction tools that promote fat loss:
- Breathwork and deep diaphragmatic breathing: Even 2–3 minutes can shift your body from a sympathetic (“fight or flight”) to a parasympathetic (“rest and digest”) state. Apps like Breathwrk or Calm are great starting points.
- Mindful movement: Activities like mobility workouts, walking, or light stretching help regulate cortisol without stressing the nervous system.
- Time in nature: Walking outdoors, especially in the morning, helps regulate your circadian rhythm and improve serotonin and melatonin production.
- Prayer, journaling, or meditation: These practices create mental space and improve emotional regulation—lowering baseline stress levels over time.
The key is consistency. Even just 10–15 minutes daily of intentional stress management can significantly support fat-burning hormones and metabolic resilience.
The Synergy of Lifestyle Regulation for Fat Burning
When you consistently sleep well and manage stress effectively, fat loss becomes easier—because you’re no longer fighting against your biology.
- You’ll naturally eat less without feeling restricted
- You’ll have more energy for workouts and movement
- Your body will prioritize fat oxidation over storage
Lifestyle isn’t a “bonus” to fat loss—it’s the foundation.
Prioritize these behaviors like you would your workouts and nutrition, and you’ll unlock the kind of sustainable transformation most people never achieve.
Step 5.) Be Consistent, Not Perfect
The biggest mistake people make when trying to burn fat? Starting strong and quitting early.
Instead, adopt a mindset of consistency over perfection.
One “bad” meal or missed workout doesn’t ruin your progress—giving up does.
Track progress weekly (not daily), reassess your strategies monthly, and keep refining your plan as you evolve.
Sustainable fat burning is a long game, but the changes you make will become part of a healthier, stronger, and leaner lifestyle.
What to Avoid If You Want to Burn Fat as Fast as Possible
Burning fat efficiently isn’t just about what you do—it’s also about what you don’t do.
Certain habits, foods, and training mistakes can sabotage fat loss by disrupting hormones, slowing metabolism, or increasing fat storage.
Avoiding these common pitfalls can accelerate your fat loss efforts, improve body composition, and help you build a leaner, stronger, and healthier physique—faster and more sustainably.
Crash Dieting or Severe Calorie Restriction
Drastically slashing calories may lead to short-term weight loss, but it often causes muscle loss, metabolic slowdown, and increased hunger hormones—making long-term fat loss harder.
Excessive Cardio Without Resistance Training
Too much cardio without strength training can accelerate muscle breakdown and lower resting metabolic rate. Prioritize lifting weights to maintain lean mass and burn more calories at rest.
Overeating “Healthy” Processed Foods
Protein bars, nut butters, and organic snacks may seem clean, but they’re often calorie-dense and easy to overconsume. Even healthy foods can stall fat loss when eaten in excess.
Inconsistent Sleep Patterns
Poor sleep impairs insulin sensitivity, increases cortisol, and raises ghrelin levels—leading to more fat storage and stronger cravings the next day.
High Alcohol Intake

Alcohol disrupts weight loss and fat oxidation, lowers testosterone, increases cortisol, disrupts sleep, and often leads to excess calorie consumption.
Even moderate intake can impair your ability to stay in a deficit.
Ignoring Stress Management
Chronic stress elevates cortisol, which promotes abdominal fat storage and reduces recovery.
Managing stress through breathwork, prayer, walking, or mindfulness improves hormonal balance and fat-burning potential.
Skipping Meals or Over-Fasting
Going too long without food can backfire by triggering binge eating later, reducing training intensity, and increasing muscle breakdown. If you use intermittent fasting, pair it with smart nutrient timing.
Drinking Liquid Calories
Juices, sweetened coffees, and even smoothies can pack in hundreds of calories without providing real satiety.
Stick to water, herbal teas, or zero-calorie drinks to stay hydrated and lean.
Final Thoughts: The Best Ways to Burn Fat as Fast as Possible

Burning fat fast isn’t about gimmicks—it’s about mastering the fundamentals and executing them consistently.
When you combine a calorie-controlled, nutrient-dense diet with resistance training, smart cardio, daily movement (NEAT), quality sleep, and effective stress management, you create the ideal internal environment for accelerated fat loss that lasts.
Here’s the proven blueprint:
- Lift weights 2–4 times per week to preserve lean muscle and boost metabolism
- Incorporate LISS and HIIT cardio to increase fat oxidation and caloric burn
- Prioritize protein and fiber-rich foods to stay full and maintain a calorie deficit
- Support your gut microbiome and digestive health with prebiotic and probiotic foods
- Hydrate, sleep 7–9 hours per night, and regulate stress to optimize hormonal balance
Supplements like magnesium glycinate, green tea extract, and high-quality protein powders can support your routine, but no product replaces the power of a consistent, sustainable strategy.
Remember—fast fat loss doesn’t mean reckless fat loss. The goal isn’t just to drop weight quickly, but to retrain your body to burn fat more efficiently, build habits you can sustain for life, and feel better in your skin every step of the way.
Burning fat fast becomes simple when your lifestyle supports it.
You don’t have to do everything at once—but you do have to start.
















